| Japanese | English |

Design Specification
1. Purpose2. Design enviroment
3. Principle
3-1. Template matching
3-2. Algorithm
4. Challenge
19th LSI Design ContestsĀEin Okinawa Design Specification - 3
3-1. Template matching
The template matching method, It is compared with the search image the small image called template image from the upper
left in the order of the lower right. And it calculated the similarity of the two images. In general, using the pixel value
as an indicator of the degree of similarity. There are several ways of calculating the degree of similarity, but this time
we will use the SAD is capable of high-speed operation.
ĀESAD(Sum of Absolute Difference)
SAD is a sum of all the values of the absolute value of the difference between the pixel values of the search image and the template image. Since the circuit can be implemented only by addition and subtraction, it is possible to perform easy and fast operations. I(x,y) stand for the x row y column of the search image, T(x,y) stand for the x row y column of the template image. Then the SAD can be represented by the following equation.
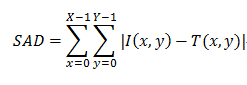
The smaller the value of the SAD, it shows that there is a high degree of similarity of the template image and the search image. The value of the SAD become 0 if the match exactly.