| Japanese | English |

15th LSI Design Contests・in Okinawa Design Specification - 2
3-2. Fast Fourier Transform
FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) is an algorithm, which speeds up the calculation of the discrete Fourier transform. It was proposed by John James Cooley in 1965.
The algorithm is described as follows
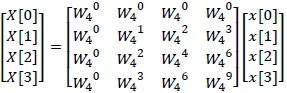
For example, in case of N=4, the matrix representation of the discrete Fourier coefficients is shown as equation (1.3).
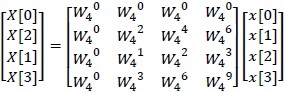
By even-odd sorting the index of the input column X[k], the following eq. (2.1) is obtained
Here, we consider about the property of the twiddle factor. The twiddle factor has the periodic property as be shown in equation (2.2)
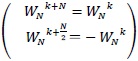
The proof of equation (2.2) is as follows.
The left-side of equation (2.2) is rewritten as following equation:
The N power of the twiddle factor ![]() is :
is :
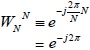
According to the Euler's identity ![]() , we have
, we have![]()
Accordingly,
Therefore,
Calculating in the same way, the N/2 power of the twiddle factor ![]()
Therefore,
Equation (2.1) is represented by using the periodic property of the twiddle factor ![]() as follow:
as follow:
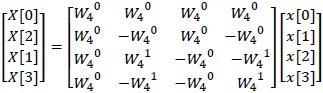
This matrix decomposes (2.4) because coefficient matrix (2.3) has the regularity.
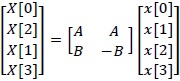
Decomposed coefficient matrix (2.4) can change as follows.
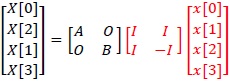
O is 2×2 zero matrix I is 2×2 identity matrix
We calculate of red part in (2.5).
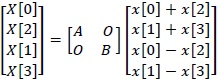
Proceed with further calculations become to (2.7).
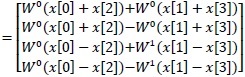
Expand (2.7)
Calculated result (2.9),(2.10),(2.11),(2.12) correspond to discrete fourier transform result (1.4),(1.5),(1.6),(1.7) use of periodicity of the twiddle factors.
DFT of N =4 needs 16 times complex multiplier and 12 times complex adder. However, in the case of (2.8) can do 4 times complex multiplier and 4 times complex adder. This algorithm is called fast fourier transform. It is specially lower complex multiplier than DFT.
(16/10/07) Correctted mistakes in Equ(2.1) and Equ(2.7)