| Japanese | English |
Design Specification
1. Purpose2. Design enviroment
3. Principle
3-1. CORDIC method
3-2. Extension to \(-â╬ü`â╬\)
3-3. Algorithm
4. Design
4-1. Design of the updated
value \(â┐_i\) and \(â┬_i\)
4-2. Judgement of the angle \(z\)
by the angle \(âĂ\)
4-3. Determination of the
initialvalue \(x_0\)
4-4. Output example of the
value
5. Example to Level2
6. Challenge
7. Unit of measurement of the
circuit scale and speed
18th LSI Design ContestsüEin Okinawa Design Specification - 4-1
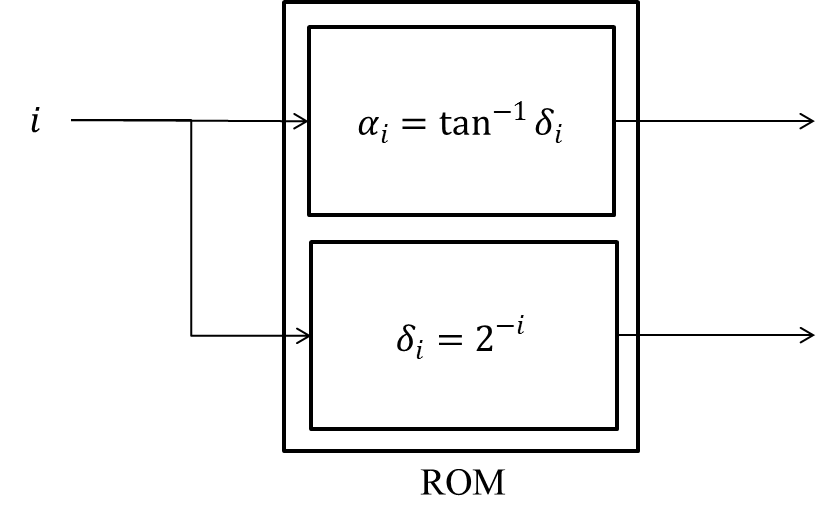
4-1. Design of the updated value \(â┐_i\) and \(â┬_i\)
Using the update value \(â┐_i\) is for the CORDIC method, it is brought close to the angle \(âĂ \) to be obtained. Updated value is defined by \(â┬_i\), as shown in (1.6) formula.The re-defined as follows when designing the hardware of the \(â┬_i\).

To redefine also \(â┐_i\) using (4.1) this equation.

And to define the value in this way, faster computation is possible in the case of performing binary multiplication with \(â┬_i\) in the conversion type, in addition to the representation can be easily fixed point, and using a shift operation is for. In the example circuit, for the construction of the circuit by the determination of the angle \(z \) which will be described later, a value in consideration of the point operations \(tan^(-1)\) is difficult in hardware, pre-calculated to (4.2) equation (4.1) wherein I stored in the ROM. In addition, both should be a positive value the value to be stored in the ROM.
i indicates the number of iterations, a value corresponding to the input i is output from the ROM.