| Japanese | English |
Design Specification
1. Purpose2. Design enviroment
3. Principle
3-1. CORDIC method
3-2. Extension to \(-ÉőĀ`Éő\)
3-3. Algorithm
4. Design
4-1. Design of the updated
value \(ÉŅ_i\) and \(ɬ_i\)
4-2. Judgement of the angle \(z\)
by the angle \(É∆\)
4-3. Determination of the
initialvalue \(x_0\)
4-5. Output example of the
value
5. Example to Level2
6. Challenge
7. Unit of measurement of the
circuit scale and speed
18th LSI Design ContestsĀEin Okinawa Design Specification - 4-2
4-2. Judgement of the angle \(z\) by the angle \(É∆\)
Described in principle in the CORDIC method and how the angle \(É∆\) to be determined or is brought close. It must be noted on designing It is the angular relationship \(z\) and the angle \(É∆\). Angle \(z\) approaches gradually to the angle \(É∆\), but may still pass the angle \(É∆\). Update value \(ÉŅ_i\) becomes negative to return the angle passed at this time. I shown below this relation.
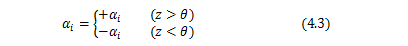
At this time, you are also involved value of \(ɬ_i\).
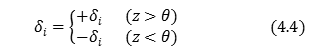
It is shown in Figure 6 To illustrate these circuits.
Copyright (C) 2014-2015 LSI Design Contest. All Rights Reserved.