| Japanese | English |
Design Specification
1. Purpose2. Design enviroment
3. Principle
3-1. CORDIC method
3-2. Extension to \(-Î`Î\)
3-3. Algorithm
4. Design
4-1. Design of the updated
value \(¿_i\) and \(Â_i\)
4-2. Judgement of the angle \(z\)
by the angle \(Æ\)
4-3. Determination of the
initialvalue \(x_0\)
4-4. Output example of the
value
5. Example to Level2
6. Challenge
7. Unit of measurement of the
circuit scale and speed
18th LSI Design ContestsEin Okinawa Design Specification - 4-3
4-3. Determination of the initialvalue \(x_0\)
It has been described for the CORDIC method circuit so far, but the problem about the initial value exists in the CORDIC method.


When determining the final value (1.14) in (1.15) formula, it is that it must be divided by the \(K_n\) \(x_0\). The accuracy is deteriorated When dividing, avoiding the use is required. To do this, I can be considered a method of choosing the initial value \(x_0\) such that \(K_n x_0=1\).
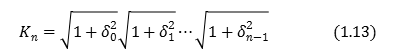
In order to determine the initial value of x, it is calculated in advance the approximation of equation (1.13),

Is obtained by calculating the (4.5) equation. NNecessary to perform the division of the output circuit by using this initial value is eliminated. Is shown in Figure 7 is a circuit diagram obtained when the (4.5) equation and the initial value. In addition, parameters used in Figure 7 is as follows.


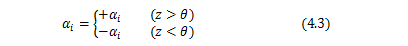
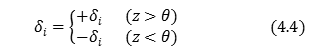
It is expected to upload at a later date Cordic circuit that RTL description actually.
